Facilities engineers, also referred to as maintenance engineers, are professionals who provide a variety of engineering and construction support for operations and buildings. You will find their tasks include planning and implementing procedures, making recommendations for repairs and upgrades, and organizing routine and emergency maintenance. A wide range of engineering disciplines can play a part in their role, including electrical, mechanical, and plumbing. Their technical skills are not only complemented by their understanding of construction law and safety standards.
Facilities engineers can start at the entry-level and quickly move up to more senior roles. It is important to have a solid portfolio that includes research, articles, and engineering projects. Facilities engineers should keep learning about their specialization. This will enable them to stand out in a job application.
A professional engineer certification is an advantage for those who apply for new positions, even though it's not mandatory. A professional engineer should have an extensive knowledge of engineering principles. A facility engineer, for example, should have knowledge of asset reliability-centered and predictive maintenance strategies as well as the design of facilities.

Facility engineers work in offices, construction, and manufacturing environments. They are responsible for ensuring that utility systems run safely, efficiently, and effectively. Facilities engineers often work in close collaboration with management and other engineers to help create efficient work schedules, and handle any problems that may arise.
A facilities engineer's responsibilities will vary based on the size and type of facility he or she is assigned to work in. The job requires good time management skills and problem-solving skills. It also requires the ability to work well in a team environment. On a typical working day, a facilities manager may be responsible for hundreds of tasks. He or she may be responsible for electrical, mechanical, or plumbing equipment, and must be able to troubleshoot issues and fix malfunctions.
Many websites, including that of the Association of Facility Engineers(AFE), provide information and news on the profession. These websites provide information such as a sample resume, salary information and articles about job opportunities.
You can also find articles and books on facilities engineering, as well as training courses and networking opportunities. In order to be a successful facilities engineer, you should have good organizational skills, a good understanding of various engineering and construction disciplines, and a solid understanding of building and safety codes.

It is important to remember that even the most skilled facilities engineers can analyze data and complete multiple tasks simultaneously. For this to happen, they will need to have a working knowledge about AutoCAD as well construction techniques such the CAM. You will also benefit from skills such as project management, critical thinking and problem solving.
One of the biggest advantages of a facilities engineer job is the chance to work with a large array of people. These engineers are skilled in working with various materials and are able coordinate the work of other engineers.
FAQ
How can we reduce manufacturing overproduction?
Better inventory management is key to reducing excess production. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. By doing this, we could free up resources for other productive tasks.
One way to do this is to adopt a Kanban system. A Kanban board is a visual display used to track work in progress. A Kanban system allows work items to move through several states before reaching their final destination. Each state is assigned a different priority.
To illustrate, work can move from one stage or another when it is complete enough for it to be moved to a new stage. But if a task remains in the beginning stages it will stay that way until it reaches its end.
This helps to keep work moving forward while ensuring that no work is left behind. Managers can monitor the work being done by Kanban boards to see what is happening at any given time. This data allows them adjust their workflow based upon real-time data.
Lean manufacturing can also be used to reduce inventory levels. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating waste from all stages of the production process. Anything that does nothing to add value to a product is waste. These are some of the most common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Excess materials
Manufacturers can increase efficiency and decrease costs by implementing these ideas.
Is it possible to automate certain parts of manufacturing
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians created the wheel thousands years ago. Robots are now used to assist us in assembly lines.
There are many uses of robotics today in manufacturing. These include:
-
Automated assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
There are many other examples of how manufacturing could benefit from automation. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
How does a Production Planner differ from a Project Manager?
A production planner is more involved in the planning phase of the project than a project manger.
What does it take for a logistics enterprise to succeed?
To run a successful logistics company, you need a lot knowledge and skills. Effective communication skills are necessary to work with suppliers and clients. You should be able analyse data and draw inferences. You need to be able work under pressure and manage stressful situations. To improve efficiency, you must be innovative and creative. To motivate and guide your team towards reaching organizational goals, you must have strong leadership skills.
You should also be organized and efficient to meet tight deadlines.
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. No. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
How does manufacturing avoid bottlenecks in production?
Production bottlenecks can be avoided by ensuring that processes are running smoothly during the entire production process, starting with the receipt of an order and ending when the product ships.
This includes both planning for capacity and quality control.
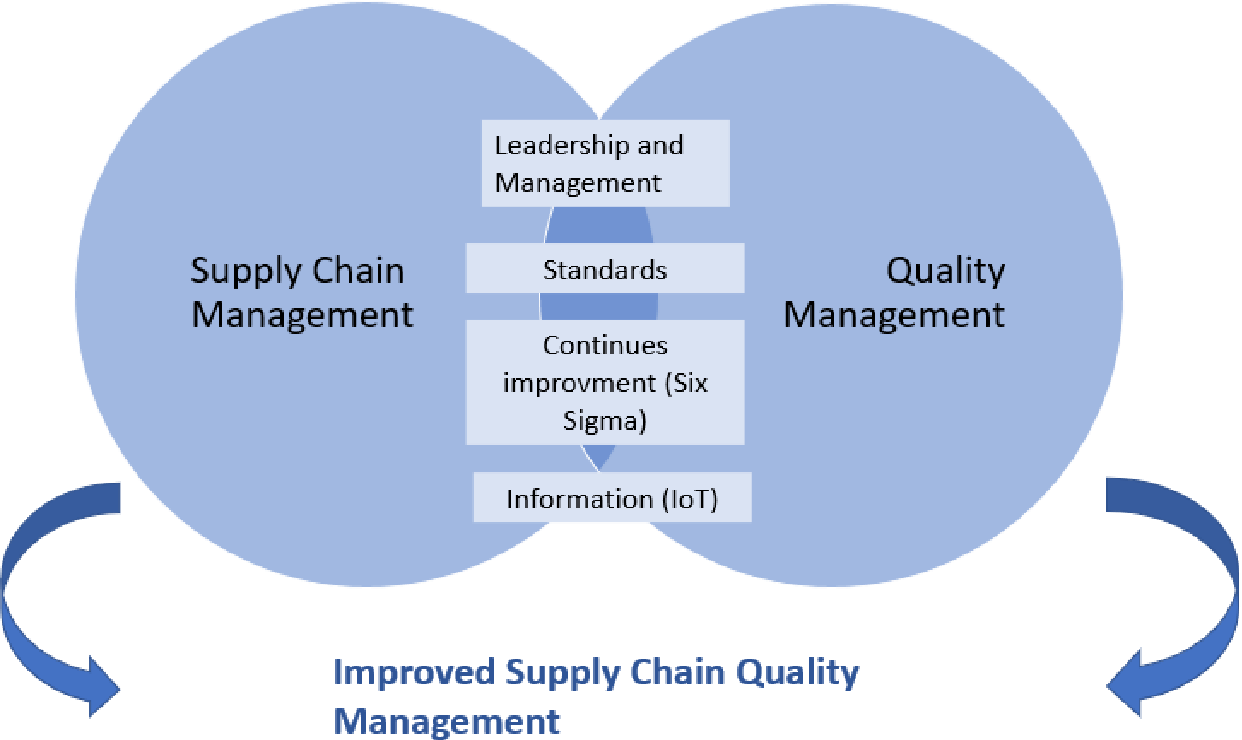
Continuous improvement techniques such Six Sigma can help you achieve this.
Six Sigma is a management method that helps to improve quality and reduce waste.
It emphasizes consistency and eliminating variance in your work.
Statistics
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma and Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined by "the application SPC (statistical process control) techniques to achieve continuous improvements." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department developed it at their Tokyo plant in Japan in 1986. Six Sigma is a method to improve quality through standardization and elimination of defects. Since there are no perfect products, or services, this approach has been adopted by many companies over the years. Six Sigma seeks to reduce variation between the mean production value. It is possible to measure the performance of your product against an average and find the percentage of time that it differs from the norm. If there is a significant deviation from the norm, you will know that something needs to change.
The first step toward implementing Six Sigma is understanding how variability works in your business. Once you understand this, you can then identify the causes of variation. Also, you will need to identify the sources of variation. Random variations occur when people do mistakes. Symmetrical variations are caused due to factors beyond the process. For example, if you're making widgets, and some of them fall off the assembly line, those would be considered random variations. If however, you notice that each time you assemble a widget it falls apart in exactly the same spot, that is a problem.
Once you identify the problem areas, it is time to create solutions. This could mean changing your approach or redesigning the entire process. You should then test the changes again after they have been implemented. If they don’t work, you’ll need to go back and rework the plan.