Supply chain risk management can be a crucial component of maintaining a stable operation, whether you run a small company or the enterprise arm a large corporation. The risks range from the simple to the very serious. Your organization can be protected from losses with a well-planned plan and an effective implementation strategy.
Data sharing is an integral part of a supply chains continuity plan. If you rely on one supplier, your organization is more vulnerable to supplier problems and vendor disputes. You will be more likely to avoid supply interruptions if your company is part-of a multisupplier group. You may also be able to negotiate an alternative supplier.
Similarly, if your company has a complex network of contractors, you are at greater risk of vendor fraud, duplicate billing, and improper related-party billing. You can create a risk assessment method to help reduce these risks. This can include a thorough assessment of your partners, suppliers, and other tier-one components.

First, identify the critical elements of your supply chain. Next, measure and quantify them. Finally, create an action program. It should include all of the above and a few other items. Proactive monitoring systems are the most important aspect. Your executives need to have real-time, accurate data about supply chain risk. You can make better decisions and react quickly by monitoring supply risk in real-time.
You must keep in mind that your supply-chain's resilience depends on how well you manage it. Particularly, you must consider the role and responsibilities of stakeholders. If the company had properly scoredcarded its suppliers, it could have prevented the supply-chain disruption that resulted in the bankruptcy of a supplier in the pharmaceutical industry.
The first step to reducing supply chain disruptions is having a plan. However, implementing the right contingency plans is not always easy. Many businesses fail to take the time to develop an appropriate number of contingency plans for each risk they are managing. These plans should be designed to have the highest possible impact.
The PPPR (preventive preparation, response, and recovery) is a standard worldwide for supply chain risk management. It is a robust approach that can improve your ability to monitor and react to supply-chain disruptions, and is often used in conjunction with other strategies to protect your organization from risk. Using a PPPR for guidance can make all the difference in whether your company survives or thrives in today's competitive market.
It is possible to get the right information from your suppliers to help you understand their history and offer. This can inform your decision-making, whether you are looking to expand your sourcing efforts or you are just fine-tuning your current processes. You can provide the right risk premiums to your insurers by having reliable data.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. E-commerce has increased the demand for quicker delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. Technology is essential for warehouses to be able to adapt quickly to changing needs. Automating warehouses is a great way to save money. These are just a few reasons to invest in automation.
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Accuracy is improved
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies to scale more easily
-
Workers are more productive
-
Provides visibility into everything that happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reduces downtime and improves uptime
-
Ensures quality products are delivered on time
-
Removes human error
-
Helps ensure compliance with regulations
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
The 7R's of Logistics is an acronym for the seven basic principles of logistics management. It was developed by International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL), and published as part of their "Seven Principles of Logistics Management Series" in 2004.
The acronym consists of the following letters:
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable - You can have confidence that you will fulfill your promises.
-
Be responsible - Use resources efficiently and avoid wasting them.
-
Realistic – consider all aspects of operations, from cost-effectiveness to environmental impact.
-
Respectful: Treat others with fairness and equity
-
Resourceful - look for opportunities to save money and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
What does manufacturing mean?
Manufacturing Industries are companies that manufacture products. These products are sold to consumers. To accomplish this goal, these companies employ a range of processes including distribution, sales, management, and production. These companies produce goods using raw materials and other equipment. This covers all types of manufactured goods including clothing, food, building supplies and furniture, as well as electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles and pharmaceuticals.
What are the logistics products?
Logistics are the activities involved in moving goods from point A to point B.
They encompass all aspects transport, including packaging and loading, transporting, storage, unloading.
Logisticians ensure that the product is delivered to the correct place, at the right time, and under safe conditions. They help companies manage their supply chain efficiency by providing information on demand forecasts, stock levels, production schedules, and availability of raw materials.
They also keep track of shipments in transit, monitor quality standards, perform inventories and order replenishment, coordinate with suppliers and vendors, and provide support services for sales and marketing.
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
How important is automation in manufacturing?
Not only are service providers and manufacturers important, but so is automation. They can provide services more quickly and efficiently thanks to automation. In addition, it helps them reduce costs by reducing human errors and improving productivity.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
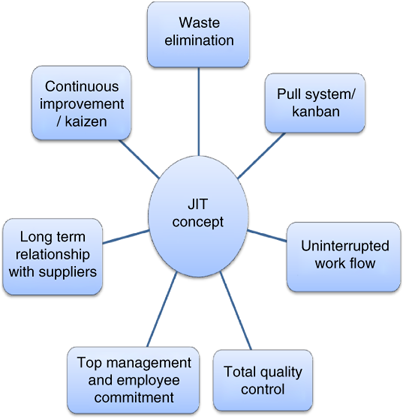
Just-intime (JIT), a method used to lower costs and improve efficiency in business processes, is called just-in-time. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means that only what you use is charged to your account. Frederick Taylor was the first to coin this term. He developed it while working as a foreman during the early 1900s. Taylor observed that overtime was paid to workers if they were late in working. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This way, you won't end up paying extra money for things that weren't really necessary.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: This is a JIT that allows you to regularly order the parts/materials necessary for your project. This will allow to track how much material has been used up. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. If you know the amount you require, you can buy the materials you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This type of JIT is most commonly used. Here you can allocate certain resources based purely on demand. You will, for example, assign more staff to deal with large orders. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This is very similar to cost-based, except that instead of looking at how much each individual worker costs, you look at the overall price of the company.
-
Material-based - This is a variant of cost-based. But instead of looking at the total company cost, you focus on how much raw material you spend per year.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of looking at the labor costs and time it takes to make a product, think about its quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. This is where you don't care about how the products perform or whether they meet customers' expectations. Instead, you're focused on how much value you add to the market.
-
Stock-based. This method is inventory-based and focuses only on the actual production at any given point. It is used when production goals are met while inventory is kept to a minimum.
-
Just-in time (JIT), planning: This is a combination JIT/supply chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. It is essential because it reduces lead-times and increases throughput.