
Ohio lost 166,000 manufacturing jobs during the Great Recession. Ohio's manufacturing sector is slowly recovering, but this has not been faster than in other states. Ohio's manufacturing jobs are still below the level they were before the recession.
Ohio's declining manufacturing job market is due to rising manufacturing competition from Europe, Japan, and Europe. Manufacturers are being forced to be more technologically-advanced and lower labor costs. Global economic conditions have been difficult, leading to job losses.
Ohio's current workforce crisis is a significant challenge for manufacturers. However, there are several initiatives in the state to address the skilled labor shortage. These initiatives are fragmented and siloed and don't address all the workforce issues manufacturers face. The Ohio Governor's Office of Workforce Transformation released a special report about the workforce shortage. It recommended greater collaboration between businesses and educators. The report revealed a disconnect between school curriculum and business requirements.

Ohio's workforce is multifaceted, complex and diverse. Manufacturing workers are less likely not to be represented by unions than workers in other industry sectors. However, unionized manufacturing jobs still offer livable wages and solid benefits.
Ohio's manufacturing industry contributes significantly to the state's economic growth. Interstate highways, railways and inland waterways allow manufacturers to efficiently distribute goods. In addition, the state ranks as a top exporter. The state also produces natural gaz, which is a big draw for private investors.
While the state has recovered 50,000 manufacturing jobs over the last four years, job gains have remained slow during Kasich's first term in office. In the first three years of his administration, manufacturing job gains averaged 7 percent. Manufacturing jobs have declined by 1,771 in the past two years. These losses can be attributed to the slowing economy and the auto industry.
Ohio is a top exporter for goods. The top export markets are the U.S.A., Canada, Mexico and the U.K. In the past year, exports decreased by $1.4 Billion. Trade policy continues to be a key issue for manufacturers in Ohio. While trade policy changes may be helpful to certain workers, they will not address the whole range of problems.
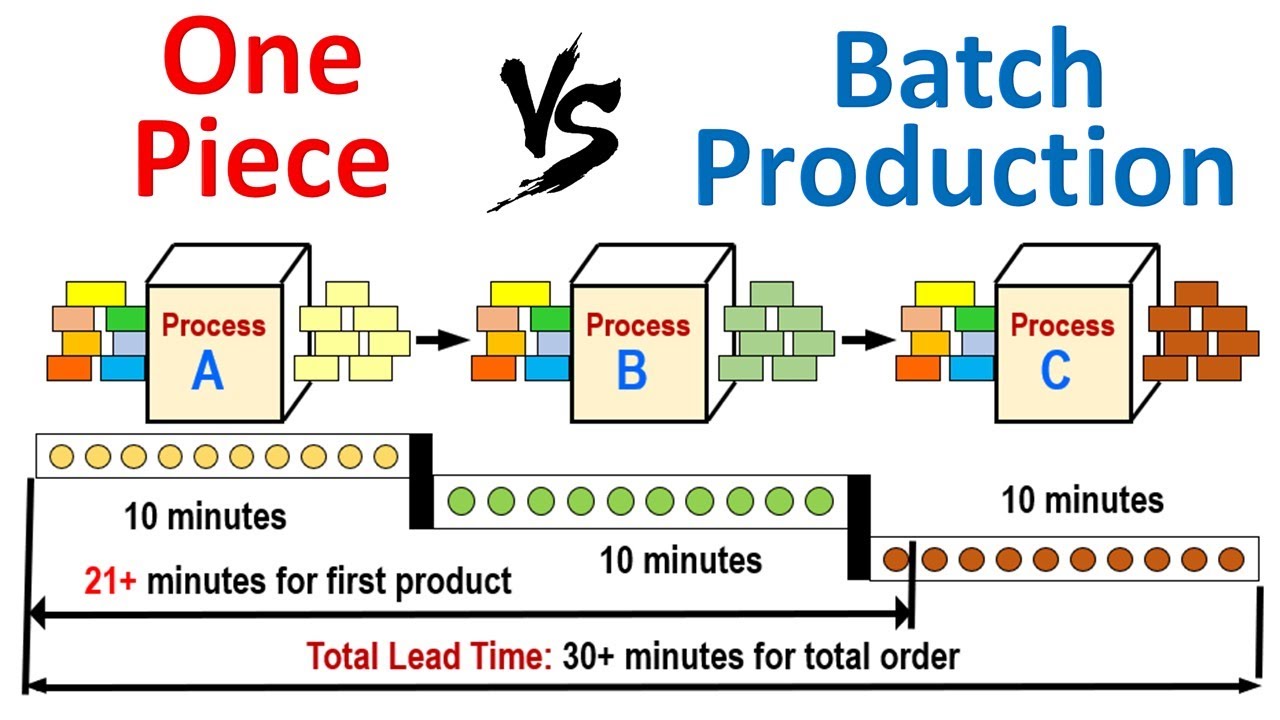
Ohio's primary industry is still manufacturing. Manufacturing jobs are some of the highest paying jobs for semi-skilled workers without post-secondary education. The wages are not keeping up with Ohio's growing production. Although manufacturing jobs pay higher than other occupations in Ohio, they are not enough for middle-class lifestyles.
Ohio's workforce in manufacturing is diverse. The state's manufacturing industries have been diversifying to match the rest of the nation. Ohio's economy has changed to be more service-oriented. Manufacturing no longer is the main employer. Manufacturers now focus more on international exposure, and developing skills for the future.
FAQ
What is the difference between manufacturing and logistics
Manufacturing refers to the process of making goods using raw materials and machines. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. Manufacturing and logistics are often considered together as a broader term that encompasses both the process of creating products and delivering them to customers.
What is it like to manage a logistics company?
It takes a lot of skills and knowledge to run a successful logistics business. Good communication skills are essential to effectively communicate with your suppliers and clients. It is important to be able to analyse data and draw conclusions. You must be able manage stress and pressure under pressure. You must be creative and innovative to develop new ideas to improve efficiency. Strong leadership qualities are essential to motivate your team and help them achieve their organizational goals.
It is important to be organized and efficient in order to meet tight deadlines.
What do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes in order to learn more about Logistics?
No. No. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
How can we reduce manufacturing overproduction?
The key to reducing overproduction lies in developing better ways to manage inventory. This would reduce time spent on activities such as purchasing, stocking, and maintaining excess stock. We could use these resources to do other productive tasks.
This can be done by using a Kanban system. A Kanban board can be used to monitor work progress. Kanban systems are where work items travel through a series of states until reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
When work is completed, it can be transferred to the next stage. It is possible to keep a task in the beginning stages until it gets to the end.
This allows you to keep work moving along while making sure that no work gets neglected. With a Kanban board, managers can see exactly how much work is being done at any given moment. This allows them to adjust their workflows based on real-time information.
Lean manufacturing is another option to control inventory levels. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating waste from all stages of the production process. Waste includes anything that does not add value to the product. Some common types of waste include:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Material surplus
These ideas can help manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Is it possible to automate certain parts of manufacturing
Yes! Yes! Automation has existed since ancient times. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. Robots are now used to assist us in assembly lines.
There are many applications for robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Automation line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots create products
Manufacturing could also benefit from automation in other ways. 3D printing makes it possible to produce custom products in a matter of days or weeks.
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It's a way to ensure that you get the right resources at just the right time. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He saw how overtime was paid to workers for work that was delayed. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
JIT is about planning ahead. You should have all the necessary resources ready to go so that you don’t waste money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. You won't have to pay more for unnecessary items.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This is a type of JIT where you order the parts/materials needed for your project regularly. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This is a type where you stock the materials required for your projects in advance. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. Here you can allocate certain resources based purely on demand. For instance, if you have a lot of orders coming in, you'll assign more people to handle them. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based: This is the same as resource-based except that you don't care how many people there are but how much each one of them costs.
-
Price-based: This is very similar to cost-based, except that instead of looking at how much each individual worker costs, you look at the overall price of the company.
-
Material-based: This is very similar to cost-based but instead of looking at total costs of the company you are concerned with how many raw materials you use on an average.
-
Time-based: This is another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing only on how much each employee is costing, you should focus on how long it takes to complete your project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each worker or how long it takes, think about how high quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT : This is the newest type of JIT. You don't worry about whether the products work or if they meet customer expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. This is used to increase production and minimize inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.