
Classical economics identifies three fundamental sectors. Manufacturing, services, and financial activities can be classified into these three categories. The classification of businesses is based on characteristics and risks. Below, you will learn more about each of the three sectors. Below is a brief overview about the types of businesses found in each sector. If you are interested, this information is available to further explore. These categories do not have to be mutually exclusive.
Economic activity
Factors used in production, inputs and outputs determine the economic activity of a country or nation. A region's economic activity is often determined by the demand for a specific good or service. There are two types of economic activity: primary and secondary. Primary economic activities provide goods or services to satisfy daily human needs, while secondary economic activities add value to raw materials and combine them to make a more valuable product. Some examples of secondary economic activities include manufacturing and processing industries.

Classification
Business classification refers the process of dividing businesses in groups based their type of activities. There are two main categories: primary and secondary. Primary businesses are those who extract and exchange natural resource. The second category of businesses processes and converts raw materials to consumer-ready products. These two types of businesses have many differences. Listed below are some of the major differences between the two types. You can use the information from this article to help you decide which type of business is best for your company.
Characteristics
Following discussion will discuss the differences in the primary, second, and third sectors. It will also focus on how each sector impacts the economy. First, let's define sectors. Sectors are unique economic entities and respond differently to different factors. These conditions can be repeated (e.g. business cycles) or one-off events (e.g. technological improvements). These characteristics can be useful for identifying the most promising sectors and determining their relative importance in an economic economy.
Risques
Industry risk is the variation in performance across industries and their companies. It is measured by the variation in return on equity and profitability. This can also be affected by stock market performance depending on the industry. For example, a company that manufactures steel is considered to be high risk because of the potential for a major earthquake in the region. These risks could help investors to determine which industries are more volatile.
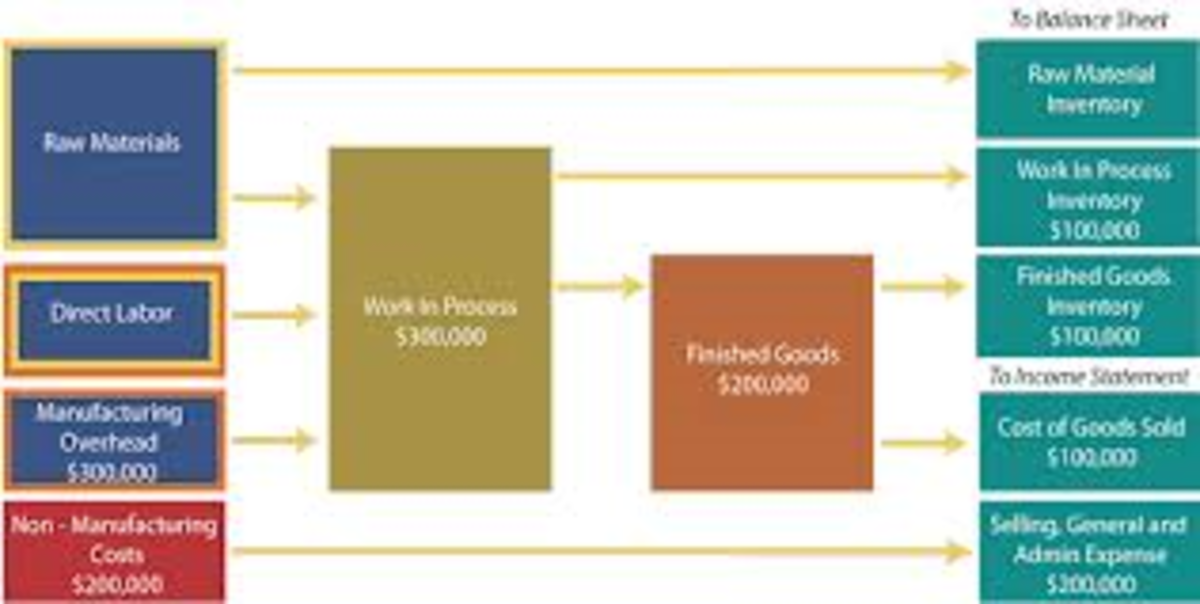
Investments
While many investors invest in specific companies, investing in sectors can be an excellent choice for the cautious investor. Sectors are more risk-free and can be found within mutual funds and exchange traded funds. Additionally, sector investing has become a very popular investment strategy. This article will show you how sector investing can help find the right investments. Learn more by reading the following. For more information, don't miss our free resource section.
FAQ
How can manufacturing excess production be decreased?
The key to reducing overproduction lies in developing better ways to manage inventory. This would reduce the amount of time spent on unnecessary activities such as purchasing, storing, and maintaining excess stock. This will allow us to free up resources for more productive tasks.
This can be done by using a Kanban system. A Kanban board, a visual display to show the progress of work, is called a Kanban board. Kanban systems are where work items travel through a series of states until reaching their final destination. Each state represents an individual priority level.
When work is completed, it can be transferred to the next stage. However, if a task is still at the beginning stages, it will remain so until it reaches the end of the process.
This allows work to move forward and ensures that no work is missed. Managers can see how much work has been done and the status of each task at any time with a Kanban Board. This information allows managers to adjust their workflow based off real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another option to control inventory levels. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste throughout the entire production chain. Anything that does not contribute to the product's value is considered waste. There are several types of waste that you might encounter:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Material surplus
These ideas will help manufacturers increase efficiency and lower costs.
What skills does a production planner need?
Being a production planner is not easy. You need to be organized and flexible. Also, you must be able and willing to communicate with clients and coworkers.
What's the difference between Production Planning & Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), or production planning, is the process by which you determine what products are needed at any given time. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling is the process that assigns dates to tasks so they can get completed within a given timeframe.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It's the process of obtaining the right amount and timing of resources when you need them. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor was the first to coin this term. He developed it while working as a foreman during the early 1900s. He noticed that workers were often paid overtime when they had to work late. He realized that workers should have enough time to complete their jobs before they begin work. This would help increase productivity.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. It is important to look at your entire project from beginning to end and ensure that you have enough resources to handle any issues that may arise. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This way you won't be spending more on things that aren’t really needed.
There are several types of JIT techniques:
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. This will allow to you estimate the time it will take for more to be produced.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. You assign certain resources based off demand. For instance, if you have a lot of orders coming in, you'll assign more people to handle them. If you don't receive many orders, then you'll assign fewer employees to handle the load.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This is very similar to cost-based but instead of looking at total costs of the company you are concerned with how many raw materials you use on an average.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based: This is one of the newest forms of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-intime (JIT), planning is a combination JIT management and supply chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.